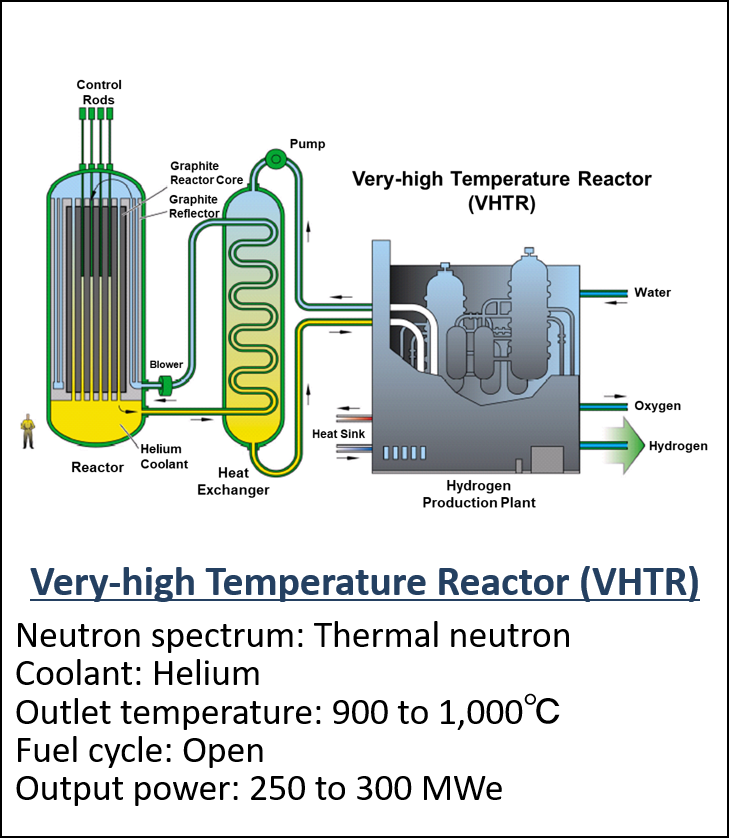
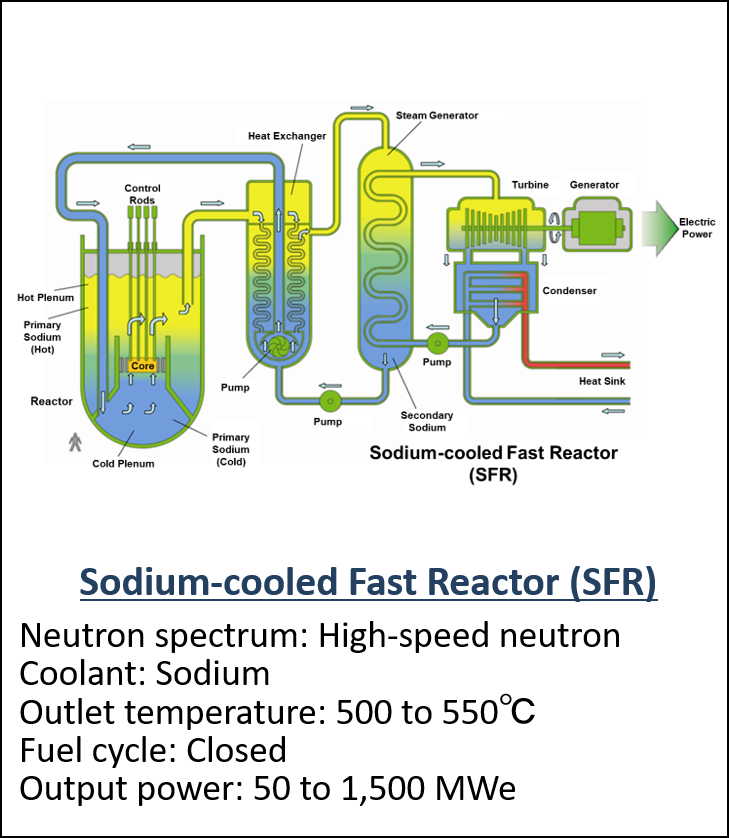
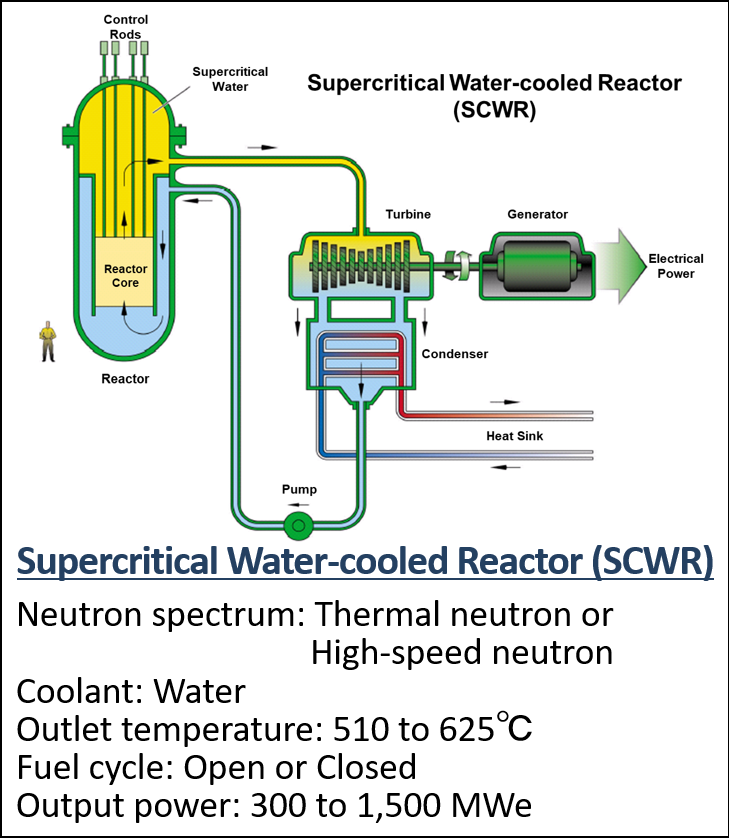
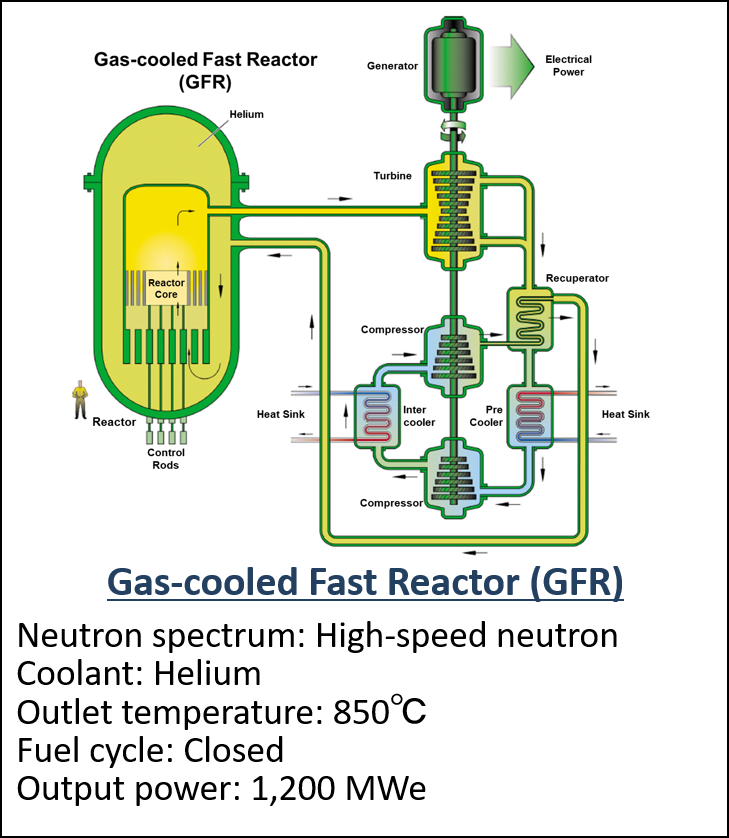
Summary of GIF organization to develop the next-generation reactors
1. What is the Generation IV International Forum?
- The Generation IV International Forum (GIF) is an international framework established in July 2001 to promote the R&D of Generation IV (Gen IV) nuclear energy systems that meet the goals described in Section 2 though multilateral collaborations.
- Current member countries as of September 2025 are 10 countries and 1 organization — Australia, Canada, France, Japan, China, Korea, South Africa, Switzerland, United Kingdom, the United States, and EURATOM.
2. What are the Generation IV nuclear energy systems?
- Gen IV nuclear energy systems are next-generation reactor concepts being developed following the first generation, which are early protocol models, the second, the existing light water reactors (LWRs), and the third, improved LWRs such as ABWR, AP1000, EPR and SMR (Fig. 1).
- GIF selected the six systems in 2002. (Fig. 2) and promoting them as innovative systems that meet the following goals.
- Sustainability
- Efficient use of fuel
- Minimum waste and its management
- Safety and reliability
- Safe, reliable operation
- Very low likelihood of core damage and minimal degree of the damage
- No need to have off-site emergency response
- Economy
- Lifecycle cost superior to other energy sources
- Financial risk comparable to other energy projects
- Proliferation resistance and physical protection
- Unattractive to terrorists because of its difficult accessibility (hard to be stolen and diverted to weapons)
- Terrorism resistant
Frequently Asked Questions about Gen IV Reactor Design
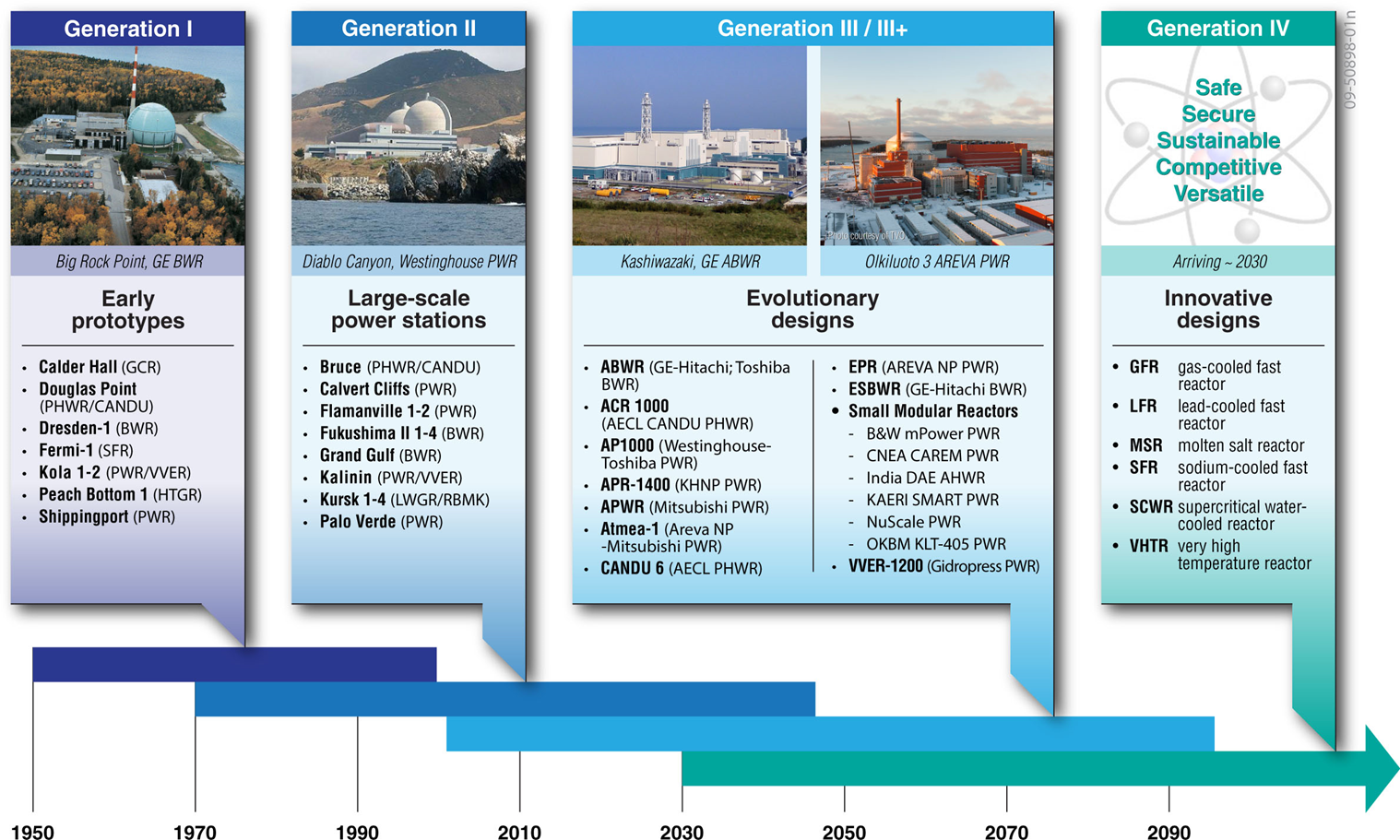
Figure 1 The generations of nuclear energy systems
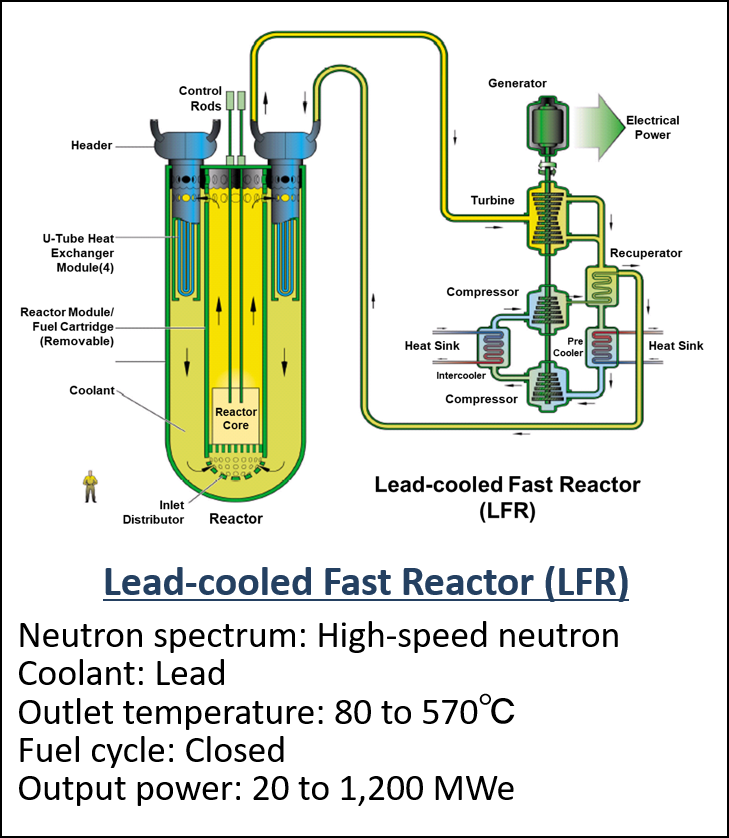
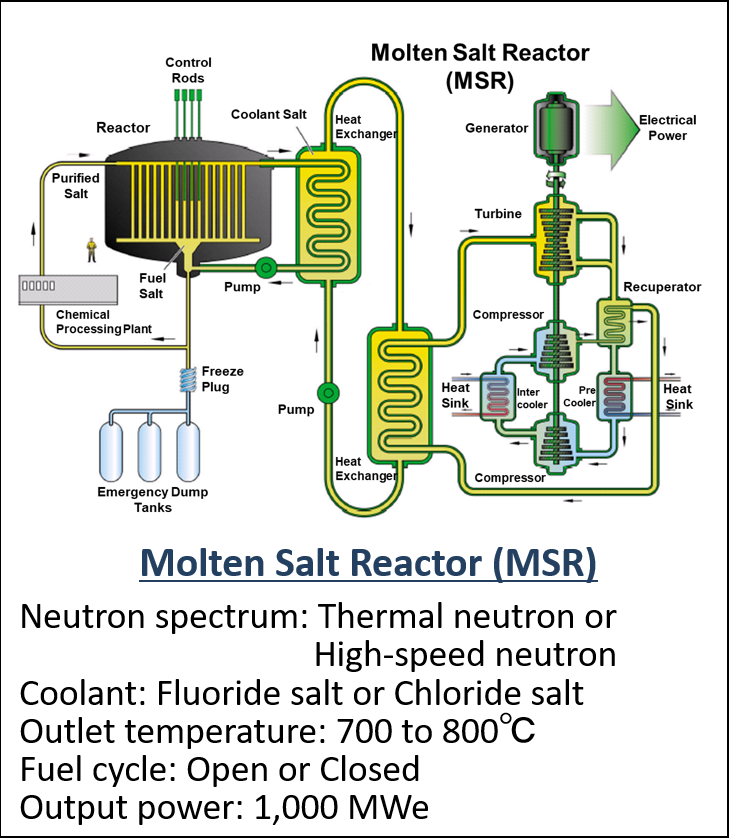
Figure 2 The six reactor technologies selected as Gen IV nuclear energy systems
3. History of GIF
| 1999 | The U.S. proposes the establishment of GIF as a framework for R&D of Gen IV nuclear energy system concepts. (Table 1) |
| Jan. 2000 | Joint statement of the GIF establishment is issued. |
| July 2001 | GIF Charter is signed, formulating the philosophy of the system development. (Table 1) |
| July 2002 | The 6 systems are selected from over 100 design concepts. |
| Dec. 2002 | The technology Roadmap is developed. |
| Feb. 2005 | Original nine countries sign the Framework Agreement (FA), the agreement that stipulates collaborative development activities to be conducted within GIF. (Table 1) |
| 2006 | They sign System Agreement (SA) on four systems out of the six, followed by other countries that become members later. The member countries sign the Project Agreement (PA) that stipulates GIF’s R&D programs. |
| 2010 | They sign memorandum of understanding (MOU) on two systems out of the six. |
| July 2011 | They agree to sign an extension of the Charter, which is set to automatically extend after this. |
| Jan. 2014 | The Roadmap is updated according to the R&D progress. |
| Feb. 2015 | The FA is extended (until February 28, 2025). |
Table 1 Member countries signed into the FA (as of January 2020)
| Members (Signed) | Implementing Organizations | Framework Agreement | System Arrangement | Memorandum | ||||
| GFR | SCWR | SFR | VHTR | LFR | MSR | |||
| Argentina | As yet unestablished | |||||||
| Australia | Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organisation (ANSTO) | Sep. 2017 | x | x | ||||
| Brazil | As yet unestablished | |||||||
| Canada | Natural Resource Canada (NRCan) | Feb.2005 | x | x | x | |||
| EURATOM | The Joint Research Center (JRC) | Feb. 2006 | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| France | Commissariat a lenergie atomique et aux energies alternatives (CEA) | Feb. 2005 | x | x | x | x | ||
| Japan | Agency for Natural Resource and Energy (ANRE (SCWR)) Japana Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) | Feb. 2005 | x | x | x | x | x | |
| Korea | Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) Korea Nuclear International Cooperation Foundation (KONICOF) | Aug. 2005 | x | x | x | |||
| China | China Atomic Energy Authority (CAEA) The Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) | Dec. 2007 | x | x | x | x | ||
| South Africa | Department of Energy (DoE) | Apr. 2008 | ||||||
| Russia | ROSATOM | Dec. 2009 | x | x | x | x | ||
| Switzerland | Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) | May 2005 | x | x | ||||
| United Kingdom | Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy (BEIS) | Oct. 2018 | x | x | ||||
| United States | Department of Energy (DOE) | Feb. 2005 | x | x | x | x | ||
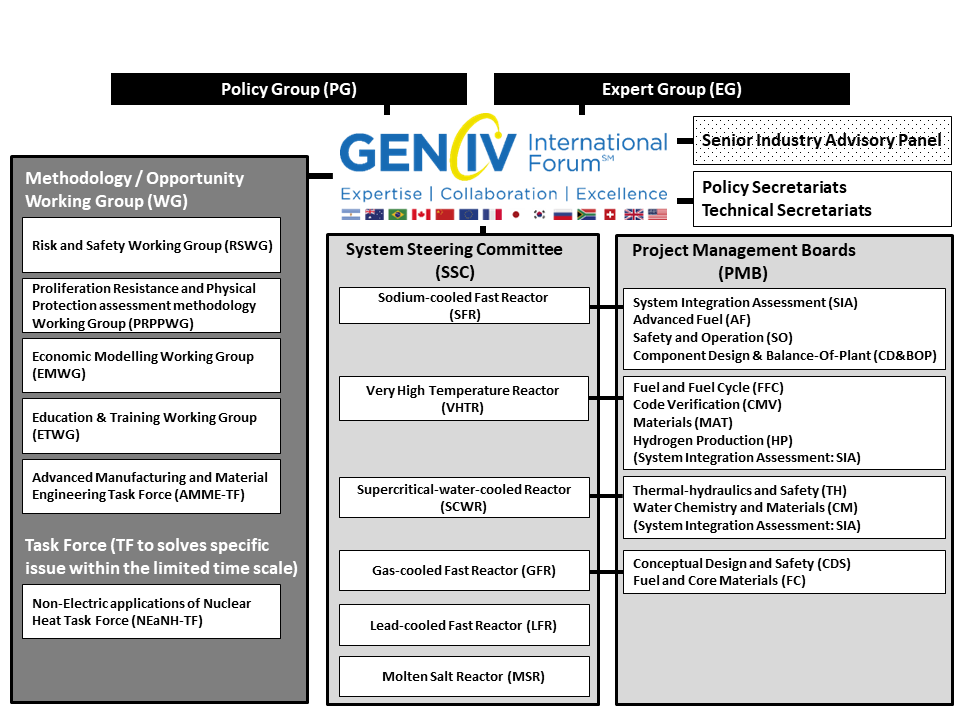
5. Governance structure (Table 2 and Fig. 4)
- Policy Group (PG) manages GIF' overall activities and operation including finance. Japan, the U.S., France, Korea and Canada serve the Chair or Vice Chairs and lead the member countries.
- Expert Group (EG) provides technical advice and counsel to PG.
- System Steering Committee (SSC), formed under each of the six systems, plans and monitors R&D of each of the systems.
- Project Management Board (PMB), formed under each of the six systems, plans R&D of each of the systems.
- Methodology Working Group (MWG) examines and promotes the development of cross-cutting evaluation methodologies on economic modeling, proliferation resistance and protection, risk and safety, education and training, and Advanced Manufacturing and Material Engineering.
- Policy Secretariat (PS) assists PG and EG, and Technical Secretariat assists SSC, PMB, and MWG.
- Senior Industry Advisory Panel (SIAP) reviews Gen IV system developments and/or advises development directions from industrial point of views.
- Task Force (TF), formed for a limited time, addresses issues on the basis of PG’s discussions. There is currently Non-Electric Applications of Nuclear Heat (NEaNH).
Table 2 Functions of the groups
| Groups | Roles |
| Policy Group (PG) | PG makes decisions on the whole future GIF directions and administrations including finance, and is responsible for relation with other organizations. |
| Expert Group (EG) | EG reviews the progress of each reactor system development and Methodology/Opportunity Working Group activities, and also discuss new emerging factors to develop Gen IV systems. |
| Senior Industry Advisory Panel (SIAP) | SIAP advises GIF activities from industries point of views toward commercialization of reactor systems. |
| System Steering Committee (SSC) | SSC develops the reactor system based on System Research Plan. Provisional SSC keeps information exchange based on MoU (Memorandum of Understanding). Provisional SSC becomes official SSC after establishing System Arrangement with System Research Plan. |
| Project Management Board (PMB) | PMB plans, reviews, and carries out each project R&D according to System Research Plans under the support of SSC. |
| Methodology/Opportunity Working Group | MWG develops common Methodology as Gen IV system for 1) Risk and safety, 2) Economic Model, 3) Proliferation resistance and physical protection, and applies Gen IV Methodology to Gen IV system based on GIF goals. OWG develops opportunities for 4) Education and Training. They are permanent Working Groups. |
| Task Force (TF) | TF solves specific issue within the limited time scale. Interim TF or voluntary Gr develops Terms of Reference (ToR) to solve specific issue and TF carries out their activity based on ToR. |
| Policy Secretariat (PS) | PS assists the Chairs and organizes PG and EG meetings. |
| Technical Secretariat (TS) | TS organizes GIF meetings and handles finance. |
6. Cooperative activities with other organizations
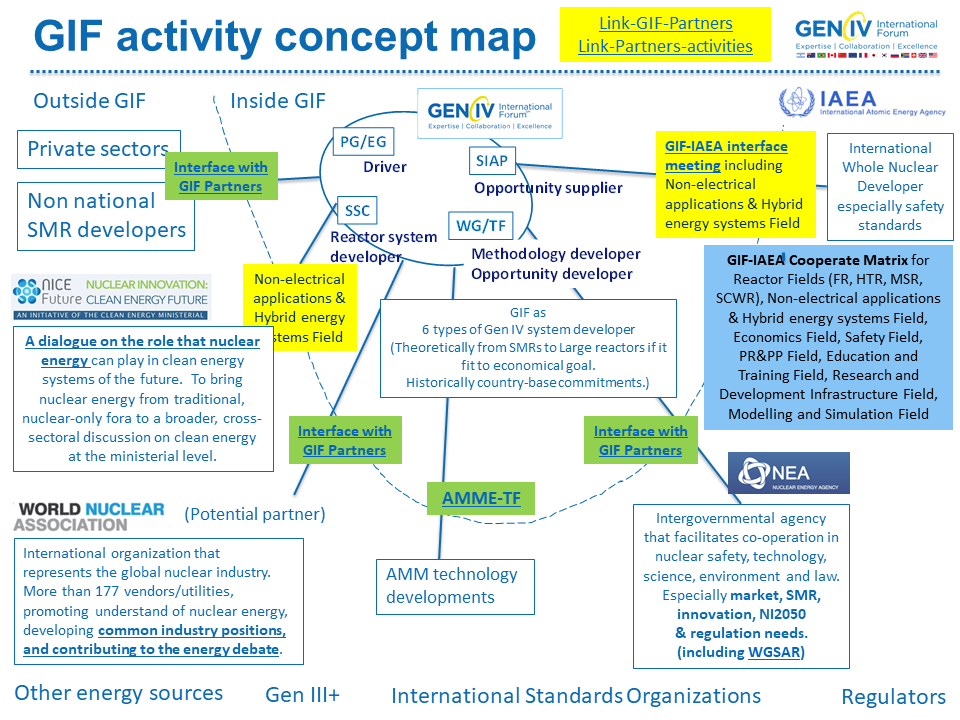
- GIF has strong cooperative activities with IAEA, OECD/NEA and CEM NICE Future(Table 3 and Fig. 5). GIF shares information of open events/webinars/publications with GIF partners to understand/offer the emerging opportunities.
GIF keeps holding open symposiums, workshops and communicates with stakeholders. Not only publishing technical documents but also sharing the stances to develop the advanced reactors with stakeholders.
Table 3 Cooperative activities with other organizations
| Organization | Activities |
| IAEA |
|
| OECD/NEA |
|
| CEM NICE Future |
|
*Click on the figure to open the pptx file.
Figure 5 GIF and GIF Partners (including a potential partners)